PCOS and Fertility
WHAT IS PCOS
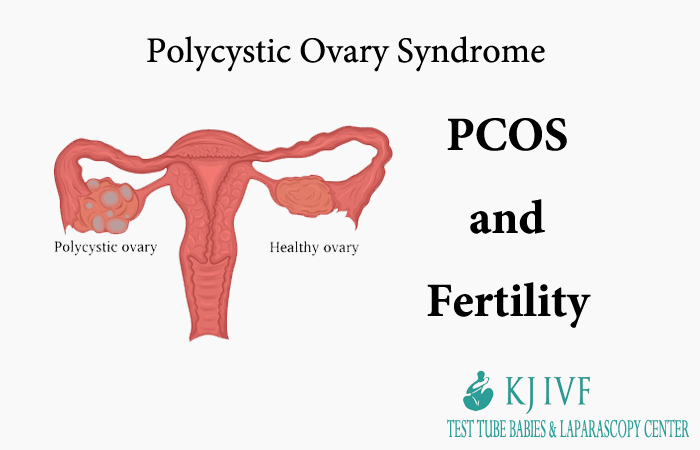
Pcos and Fertility: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is very common endocrine condition in reproductive-aged women. It affects approximately 5-10% of young women and often leads to the difficulty conceiving. Women with this condition can experience irregular periods, abnormal hair growth, acne, and can have ovaries containing the multiple small follicles.
PCOS and Infertility
With nearly one-third of all infertility diagnoses in women, polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common ovulatory disorder in women of the reproductive age. PCOS negatively impacts fertility because women with this condition do not ovulate, or release an egg, each month due to an overproduction of the estrogen by the ovaries. Because ovulation does not occur regularly, periods become irregular and the increased levels of hormones such as testosterone can affect egg quality, inhibit ovulation, lead to insulin resistance, and increase the risk of disorders such as gestational diabetes.
Can Women with PCOS get Pregnant
While myths persist that women with PCOS cannot get pregnant, the reality is that it is highly treatable and nearly every woman with the PCOS should be able to get pregnant. In fact, many women will experience increases in the fertility through lifestyle changes and modest weight loss. Others will find success with basic fertility treatment and the medications. And for those that require additional help conceiving, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is a highly effective form of treatment for women with PCOS.
What are the Symptoms of PCOS?
PCOS affects approximately 5 to 10 percent of the population, and is the most prevalent in Hispanics and African Americans. Recent studies also suggest that there is a rising rate in the women of Asian descent.
Some of the most recognizable symptoms of the PCOS include absent or irregular menstrual cycles, acne, and excessive body hair growth. While many people may consider obesity as a main symptom of the disease, approximately one-third of women with PCOS has normal weight or is underweight.
What Causes PCOS?
Although the specific cause of the PCOS is still unknown, the condition results in hormonal imbalances that curtails or prevents ovulation—the body’s process of producing and releasing eggs from the ovary. It is common for women with the PCOS to have an inappropriate production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). As a result, they experiences limited follicular development (follicles are small sac-like structures within the ovaries, and each follicle contains an egg). With limited follicular development, egg growth will not occur. Also as a result, women with the PCOS have an increase in testosterone and other typically male hormones (androgens).
Clinically, the limited egg growth may result in irregular ovulation or a complete lack of ovulation (anovulation), which can persist for months or even years. This ovulatory dysfunction is what really causes infertility in these women. Also, when an ovulation is prolonged, the endometrial tissue in the uterus can get very thick, resulting in heavy and/or irregular periods. The increase in androgens is also liable for the excess hair growth and acne.
It is also common for women with PCOS to have insensitivity to insulin. This, many times, can predispose them to have increased weight gain and the obesity that places the patient at higher risk for diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
How Can I Get Tested for PCOS And Fertility?
There are no specific tests for the PCOS, and the condition is essentially clinically diagnosed.
Your medical team will determine if there are any physical signs of excess androgens present, as well as evidence of the ovulation problems by evaluating the length and regularity of your menstrual cycles.
Some testing may also reveal the common features of the condition. For example, all patients at KJIVF undergo basic fertility testing including among others blood tests and the ultrasound. The ultrasound can determine if the ovaries are enlarged and contain immature resting follicles, a prominent sign of the PCOS. Blood testing can reveal or confirm the elevated levels of androgen (male hormones). When making a diagnosis of PCOS, it is also important to rule-out other causes of the ovulatory disorders, including thyroid dysfunction.
Once your physician has a complete the picture and can make the diagnosis, he or she will work with you to create an individualized treatment plan.
Can Diet and Exercise help Women with the PCOS Conceive?
For overweight women with the PCOS, weight loss is often the first step to increasing your chances of pregnancy. The benefits of the weight reduction include improved ovulatory function, improved chances of conception, a safer pregnancy for both the mother and baby, and—if needed—better response to fertility medications. Studies have shown that by losing just 5 % of the body weight, a woman can actually restore her menstrual cycle and ovulate on her own. Weight loss has also been shown to the reduce other symptoms such as hair growth, acne, and balding.
What Medications are Prescribed for the PCOS
For women with the PCOS who are actively trying to conceive, it is advised to consult with your fertility specialist, since many women with PCOS are not ovulating. Your physician can prescribe medication to help the stimulate ovulation.
Oral fertility medications like clomiphene citrate or the letrozole continue to be widely used to stimulate the development of an ovarian follicle containing an egg. Clomiphene citrate acts by blocking the action of the oestrogen in the brain (the hypothalamus and pituitary). As a result, there is an increased production of the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), causing the development of one or more follicles. If ovulation is still irregular and additional medications can be prescribed. Metformin for example assists to make the body more sensitive to insulin, which can result in more regular ovulation.
What Fertility & PCOS Treatments are Available?
Depending on the initial testing, a fertility expert may recommend a patient to start ovulation induction medications (cited above) with timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination (IUI) that can be scheduled around the time of the ovulation. For these treatments, it is significant that the Fallopian tubes are open and the sperm counts are normal. The typical success rate with IUI is about 15 to 25 percent per cycle; a woman’s individual success rate with the IUI is largely impacted by her age.
If ovulation induction with timed intercourse or IUI fails to achieve the pregnancy after a few attempts of this therapy, or if the patient also has other infertility factors such as the blocked Fallopian tubes, her physician may recommend in vitro fertilization (IVF).
PCOS and Fertility Treatment at KJIVF
We, at KJIVF, offer a step by step approach to treating PCOS related infertility. Obese patients requiring weight loss are counseled thoroughly to adopt lifestyle modifications including diet and exercise. After a thorough evaluation, patients are selected for IUI treatment and offered individualized protocols for ovarian stimulation. Supportive drugs like myoinositol, D- chiroinositol, and metformin are prescribed wherever required. Those patients not conceiving after adequate attempts of IUI are then counseled and taken up for IVF treatment. Treatment is offered with complete transparency and thorough discussion with the patient. We at KJIVF, offer low-cost IVF treatment to make it affordable for the patient.
For more queries, Call us at +9196507 25386, +91 011 3560 4368.